GeoVision Webcam Setup Guide (pt. 1)
:
from
to
Introduction
In order to use the WebCam feature of GeoVision there is an amount of configuration that needs to take place. As no one sites network or Internet connection are truly alike, it is difficult to write a definitive WebCam setup guide. This document will give example on widely used hardware, and hopefully give you the tools you need to configure the WebCam on an unlisted router.
Explanation of terms and technologies
WAN
Wide Area Network – For the purposes of this document you can substitute WAN for Internet, as in WAN (Internet) side of your router.
LAN
Local Area Network – Local network of PCs and network devices. To be used as LAN side of your router.
Ports
Internet traffic travels though ports. This method is used, as it can identify what sort of data the TCP packet is carrying. For instance web browsing uses port 80, email uses port 25 etc.
GeoVision uses the ports listed below for WebCam
80 HTTP Port
For the WebCam Interface in Internet Explorer (all web pages by default use port 80). When you use Internet Explorer it silently adds “:80” to the end of the webpage address, try it yourself www.worldeyecam.com is the same as www.worldeyecam.com:80
- 4550 Command Port For the commands that are sent between the interface and the GeoVision system
- 5550 Data Port For the Video Stream
- 6550 Audio Port For the Audio Stream
Transmission Control Protocol – The protocol used to guarantee that packets of data get to the correct destination, and that they are received in the correct order.
ADSL / Cable Modem
These are usually USB devices that the computer sees as a traditional dial up connection. The PC has to “dial” the Internet connection, the connection is always available, but not always connected.
ADSL Modem Router (Gateway)
These are becoming more and more common. Most ISPs now give the user a router rather than a modem.
Routers are usually connected to your computer via an Ethernet cable. A router is a device that sits between a LAN (Local Area Network) and the Internet.
Routers are far more advanced that ADSL modems, and offer the following benefits:
- Enhanced Security via a hardware firewall
- Improved connections speeds
- Always on Internet connection
- Superior reliability
Firewall
Either a piece of hardware (usually part of a router) or software used to limit unauthorized network connections into a network or computer.
Port Forwarding
Port Forwarding can also be referred to as Port Redirection, Virtual Servers or NAT (Network Address Translation). They all fundamentally do the same thing.
When you want to view your cameras, using the GeoVision WebCam feature, you open Internet Explorer and enter the WAN IP address of your router. As there may be many systems behind the router, we need to tell the router where to forward the Internet Explorer (WebCam) traffic to.
The reason for configuring the router is not just one of security, when you connect to the WAN IP address of your router, it does not know where to direct that traffic. Take the example below, there are several PCs on the network, without port forwarding, the router does not know where to send the packets.
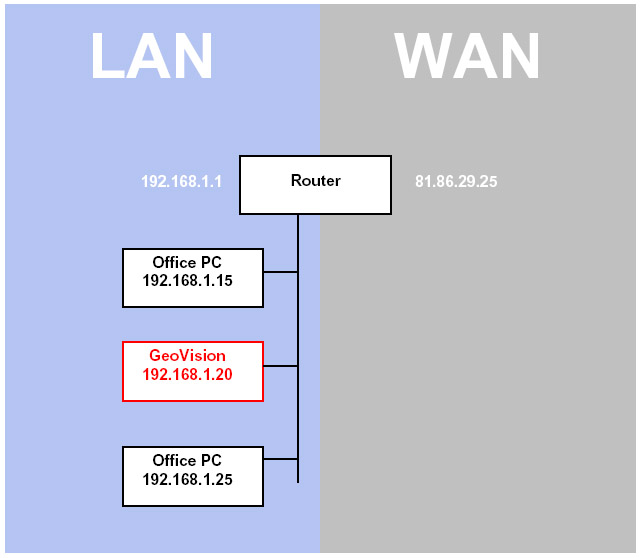
Within the router we have configured a routing table like the one below.
| EXTERNAL PORT | INTERNAL PORT | LAN IP ADDRESS |
| 80 | 80 | 192.168.1.20 |
| 4550 | 4550 | 192.168.1.20 |
| 5550 | 5550 | 192.168.1.20 |
| 6550 | 6550 | 192.168.1.20 |
When traffic hits the WAN side of the router using any of the ports listed, it looks for preconfigured routes (or forwards) and applies them, see the diagram below

| 1 2 3 | The router is hit by the request from the remote Internet Explorer for port 80, 4550 and 5550 (also 6550 is using audio) Router looks up the ports being requested, within it’s lookup table, if it finds a corresponding entry, then it will forward the traffic The traffic has been successfully forwarded to the GeoVision system (192.168.1.20) |
Configuration
Windows XP Firewall / Software Firewall
Windows XP comes with a built in software firewall. By default the Windows XP firewall will block any incoming TCP connections.
You can download Windows XP Firewall configuration scripts from the download area of our website, available at https://www.worldeyecam.com/Geovision-Software-Downloads-sp-24.html To run them, download the appropriate file for your card, unzip the file, and run the batch file. Links to the files are listed below.
N.B.
These files will only work if you have installed GeoVision to the default install directory, i.e. C:\GVxxxx
GV250
GV600
GV650
GV800
GV900
GV1000
GV1120
GV1240
GV1480
If you have installed GeoVision to an alternative directory, you will need to create exceptions for the following.
Applications
[GeoVision Install Directory]bcasttcp.exe
[GeoVision Install Directory]audioserver.exe
[GeoVision Install Directory]ccserver.exe
[GeoVision Install Directory]dmmcast.exe
[GeoVision Install Directory]rpbsvr.exe
[GeoVision Install Directory]webcamserver.exe
[GeoVision Install Directory]tcpsvr.exe
[GeoVision Install Directory]dmwebcam.exe
[GeoVision Install Directory]twinserver.exe
To create exceptions to the Windows XP firewall, you need to do the following:
1. Enter Control Panel
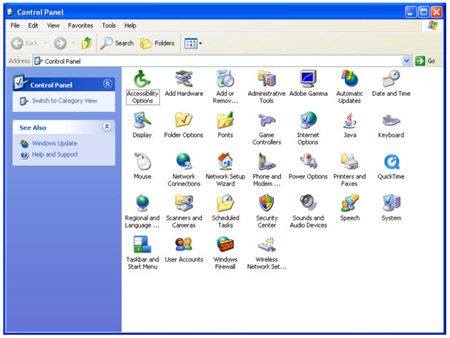
2. Double Click on Windows Firewall

3. Click on the Exceptions Tab
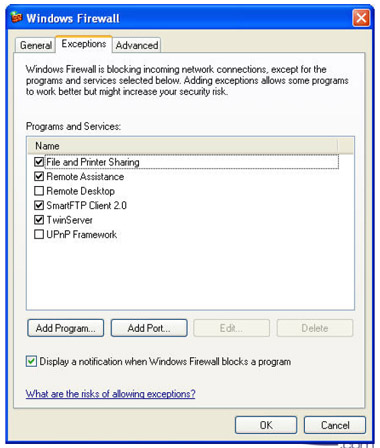
To add a Program Exception
1. Click on Add Program
2. Click on Browse
3. Navigate to the GeoVision install directory
4. Select the first program in the list above
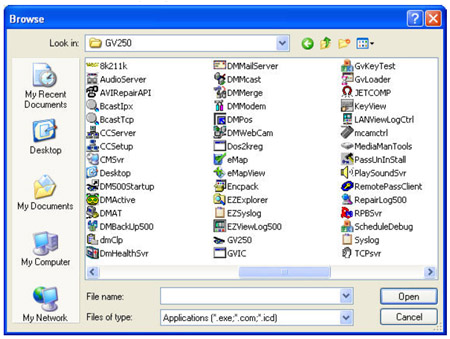
5. Click OK
Repeat steps 1 to 5 for each program in the list above
Ports
80
4550
5550
6550
To add a Port Exception
1. Click on
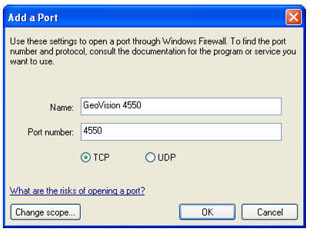
2. Give the port a name
3. Enter the first port number in the list above
4. Make sure that TCP is selected
5. Click OK
Repeat steps 1 to 5 for each of the ports listed above.
If you are using a software firewall other than Windows XP, please check your documentation about creating exceptions.
| Next page > |




